the tudor monarchs and their religion | tudor sovereigns the tudor monarchs and their religion Any study of church and state in Tudor England should take into account the importance of religion to people in the late Middle Ages, the structure and function of church and state, and .
DEPO Online. Dārzs. Sports, tūrisms un aktīvā atpūta. Mājsaimniecības un uzkopšanas preces. Auto un velo preces. Būvmateriāli. Krāsas, dekoratīvie apmetumi un gruntis. Instrumenti, darba apģērbs un darbnīcas aprīkojums. Skrūves, naglas un stiprinājumi.
0 · tudor sovereigns
1 · tudor monarchy timeline
2 · tudor monarchy family tree
3 · the tudor monarchy john guy
4 · the tudor kingdom
5 · list of tudor monarchs
6 · list of tudor kings
7 · kings of tudor
Las Vegas Raiders. 8-7, 4-4 home. 17. Gamecast. Recap. Box Score. Play-by-Play. Team Stats. Game Leaders. DEN. LV. Passing Yards. DEN. D. Lock. 15-22, 153 YDS. LV. D. .
The Tudor era witnessed the most sweeping religious changes in England since the arrival of Christianity, which affected every aspect of national life. The Reformation eventually transformed an entirely Catholic nation into a predominantly Protestant one.
People in Tudor times were very religious and were prepared to die for their beliefs. It must have been very hard for them during the 118 years the Tudor kings and Queens ruled .
tudor sovereigns
tudor monarchy timeline
The House of Tudor was an English and Welsh dynasty that held the throne of England from 1485 to 1603. They descended from the Tudors of Penmynydd, a Welsh noble family, and Catherine of Valois. The Tudor monarchs ruled the Kingdom of England and the Lordship of Ireland (later the Kingdom of Ireland) for 118 years with five monarchs: Henry VII, Henry VIII, Edward VI, Mary I and Elizabeth I House of Tudor, an English royal dynasty of Welsh origin, which gave five sovereigns to England: Henry VII (reigned 1485–1509); his son, Henry VIII (1509–47); followed .England underwent huge changes during the reigns of three generations of Tudor monarchs. Henry VIII ushered in a new state religion, and the increasing confidence of the state coincided .Any study of church and state in Tudor England should take into account the importance of religion to people in the late Middle Ages, the structure and function of church and state, and .
The Protestant religion rejected the Pope's control and wanted individual believers to have their own relationship with God rather than only through a priest. These events came after many .The Tudor dynasty ruled England from 1485 to 1603. Their story encompasses some of the most dramatic and unforgettable events in European history. And they remain the most famous and . The sixteenth century was an age of Reformation. There was religious reformation, as Protestantism came to England, Scotland and even Ireland, bringing liberation, chaos and bloodshed in its wake. And there was . From Henry VII’s usurpation of the throne in 1485 to the death of Elizabeth in 1603, Tudor monarchs relied on paintings, sculptures, tapestries and other art forms to legitimize their nascent .
Throughout the rest of the Tudor period, Tudor monarchs tried to take greater control of Ireland. The first printed translation of the whole Bible into English was published in 1535. House of Tudor, an English royal dynasty of Welsh origin, which gave five sovereigns to England: Henry VII (reigned 1485–1509); his son, Henry VIII (1509–47); followed by Henry VIII’s three children, Edward VI (1547–53), Mary I (1553–58), and Elizabeth I (1558–1603).. The origins of the Tudors can be traced to the 13th century, but the family’s dynastic fortunes were . As such, when Elizabeth died in 1603, so did the Tudor line. She reluctantly named her cousin James VI of Scotland as her heir, and so began the Stuart dynasty in England, ushering in a new era of political upheaval, flourishing court culture, and events that would alter the shape of the monarchy for good.
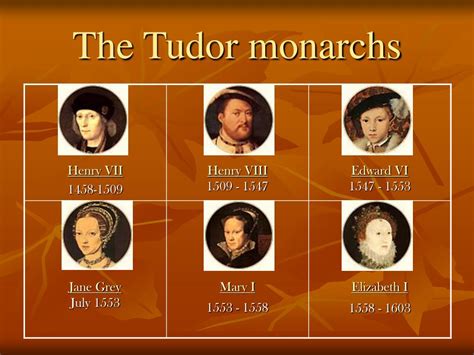
About this Site. Contact Information Henry VII 1485 - 1509. Henry VIII 1509 - 1547. Edward VI 1547 - 1553: Jane Grey July 1553The "Polytyque Churche": Religion and Early Tudor Political Culture, 1485-1516. By PETER IVER KAUFMAN. Macon, Ga.: Mercer Univer-sity Press, 1986. War, Taxation and Rebellion in Early Tudor England: Henry VIII, Wolsey and the Amicable Grant of 1525. By G. W. BERNARD. New York: St. Martin's Press, 1986. Parliament and the Crown in the Reign of .The Tudor era saw unprecedented upheaval in England. Between them the five Tudor kings and queens introduced huge changes that are still with us today. The years between the crowning of Henry VII .
Under Henry, England moved away from Roman Catholicism and towards a more Protestant theology. Henry dissolved over 800 monasteries, seizing their wealth and land. 3 This influx of capital, estimated at £1.3 million (equivalent to £500 million today), helped finance Henry‘s military campaigns and lavish court. 4 Military Exploits and Cultural Achievements End of the Tudor Dynasty . None of Henry VIII’s children had any lasting offspring of their own, and when Elizabeth I died, she was the last of the Tudor monarchs; she was followed by James Stuart from Scotland, the first of the Stuart dynasty and a descendant of Henry VIII’s eldest sister, Margaret. The Tudors passed into history. Politics was never simple in Tudor period England. In reality, England was ruled over by three bodies; the Monarchy, the Privy Council and Parliament. Although controlled by the monarchs these bodies worked together to make laws, raise money via taxes, and make decisions in regard to religion and national defense.The Tudors were a royal family reigning in Britain between 1485 and1603. Their names and the order in which they reigned: Henry VII – 1485-1509 Henry VIII – 1509-1547 Edward VI – 1547-1553 .
tudor monarchy family tree
The Tudor Monarchs. The Tudor dynasty shaped English history with noteworthy changes to politics, religion, and society. Even though the Tudors faced both internal and external threats, they managed to maintain their hold on the throne, which helped them set the stage for the eventual transition to the House of Stuart. Henry VII (1485–1509)The Tudors were a royal family reigning in Britain between 1485 and1603. Their names and the order in which they reigned: Henry VII – 1485-1509 Henry VIII – 1509-1547 Edward VI – 1547-1553 . And there was political reformation, as the Tudor and Stewart (later 'Stuart') monarchs made their authority felt within and beyond their kingdoms more than any of their predecessors. Together, these two reformations produced not only a new religion, but a new politics -absolutist yet pluralist, populist yet law-bound - and a new society .The Tudor era witnessed the most sweeping religious changes in England since the arrival of Christianity, which affected every aspect of national life. The Reformation eventually transformed an entirely Catholic nation into a predominantly Protestant one.
During the 118 year rule of the Tudors, the official religion changed four times. This article details the official religion of each of the Tudor monarchs and offers insight and explanation as to the reasoning behind each change. People in Tudor times were very religious and were prepared to die for their beliefs. It must have been very hard for them during the 118 years the Tudor kings and Queens ruled because they were often forced to change their religion depending on .
The Tudor monarchs ruled the Kingdom of England and the Lordship of Ireland (later the Kingdom of Ireland) for 118 years with five monarchs: Henry VII, Henry VIII, Edward VI, Mary I and Elizabeth I. The Tudors succeeded the House of Plantagenet as rulers of the Kingdom of England, and were succeeded by the Scottish House of Stuart .
House of Tudor, an English royal dynasty of Welsh origin, which gave five sovereigns to England: Henry VII (reigned 1485–1509); his son, Henry VIII (1509–47); followed by Henry VIII’s three children, Edward VI (1547–53), Mary I (1553–58), and Elizabeth I (1558–1603).England underwent huge changes during the reigns of three generations of Tudor monarchs. Henry VIII ushered in a new state religion, and the increasing confidence of the state coincided with the growth of a distinctively English culture.Any study of church and state in Tudor England should take into account the importance of religion to people in the late Middle Ages, the structure and function of church and state, and the intellectual, political, and religious traditions that bind the historian.The Protestant religion rejected the Pope's control and wanted individual believers to have their own relationship with God rather than only through a priest. These events came after many years.

The Tudor dynasty ruled England from 1485 to 1603. Their story encompasses some of the most dramatic and unforgettable events in European history. And they remain the most famous and controversial of royal families. Follow the links on this page .
the tudor monarchy john guy

the tudor kingdom
list of tudor monarchs
list of tudor kings
Krišjānis, Elfa, Aivita, Elvita; Kontakti; Reklāma; Ziņas ; Bizness; Life; Sports; Kultūra; Auto; Cālis; Tasty
the tudor monarchs and their religion|tudor sovereigns